What Does the Proton Pump Do in Photosynthesis
7 Where does ETC occur in photosynthesis. Transferred light energy excites P700 which loses electrons it receives from the electron.

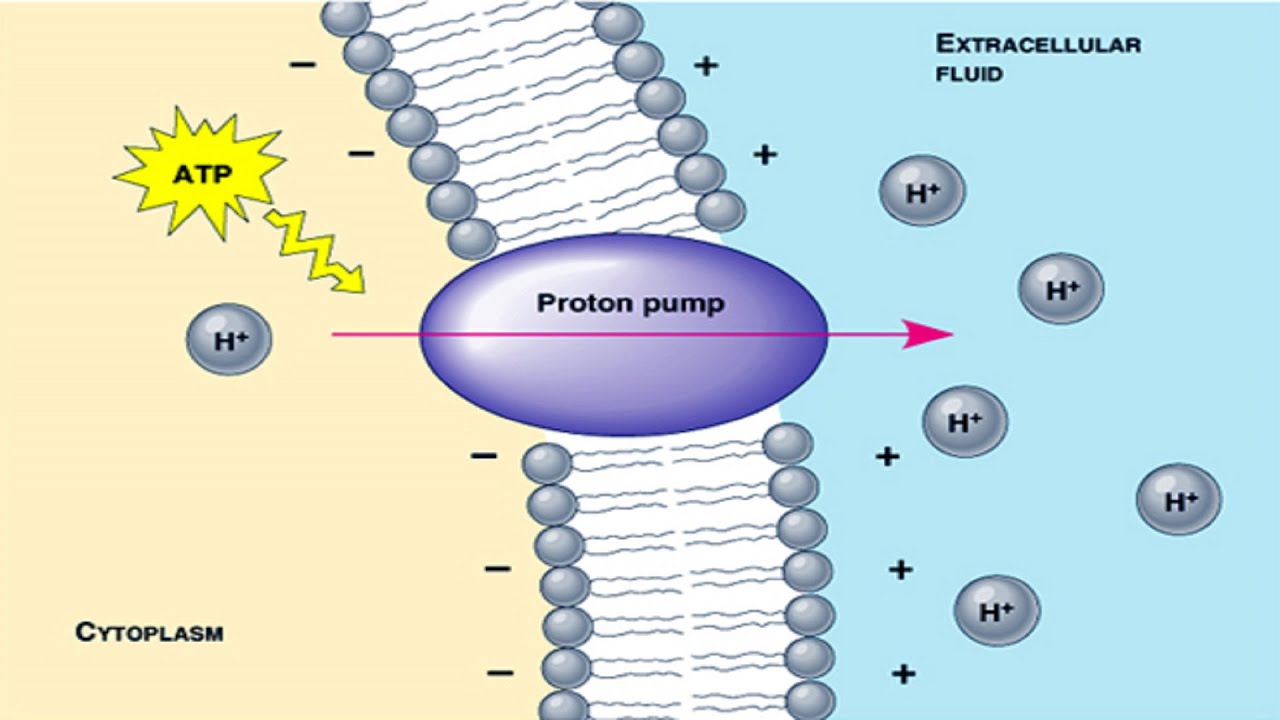
Photosynthesis Of Atp Electrons Proton Pumps Rotors And Poise Cell
This proton gradient constitutes a fundamental energy reservoir.

. The proton gradient produced by proton pumping during the electron transport chain is used to synthesize ATP. 5 What does ATP do in plants. Proton pumps are a special kind of transporter that push hydrogen ions from areas of low concentration to areas with high concentration.
12 How does etc produce ATP. This is how the proton gradient in photosynthesis helps in generating ATP. 11 How does etc make ATP.
The proton pump plays an important role in cell respiration and photosynthesis. Platoquinolplastocyanin reductase proton pump is an enzyme related to Complex III that is found in the thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts of plants cyanobacteria and green algae. That the situation in photosynthesis is similar to that for the oxidative electron transport chain.
The electron transport chain in cell respiration generates an. 7 What is the role of ATP and ADP in photosynthesis. Diffusion can then use this gradient to capture energy again as the ions move downhill.
The proton pump plays an important role in cell respiration and photosynthesis. Its working depends upon the proton gradient created in the thylakoid lumen which helps the proton molecules down the thylakoid membrane of plant cell into the chloroplast stroma. In photosynthesis the proton pump involves.
5 What is ETC function. What do proton pumps do in cells. Protons flow down their concentration gradient into the matrix through the membrane protein ATP synthase causing it to spin like a water wheel and catalyze conversion of ADP to ATP.
2 What is the role of ATP in photosynthesis. As they travel along the ETC they give up energy which is used to. A student asked if ATP is used to drive the proton pump within the thylakoid membrane only for ATP to then be produced when the proton motive force takes effect and the ATP-synthase catalyses the phosphorylation.
How does a cotransporter work. Using a Proton pump hydrogen ions are pushed from low concentration areas to high concentration ones. Ions moving down a gradient release energy but when they move up a gradient it takes energy.
4 What does the ETC do in cellular respiration. As a result of electron transport chains between cells in cells the hydrogen peroxide is generated into oxygen which powers electrochemical activity in the organ. The electron finally gets dumped on the molecule NADP Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate changing that molecule into NADPH.
Proton pumps are a special kind of transporter that push hydrogen ions from areas of low concentration to areas with high concentration. What does proton pump do. 8 Where does ETC occur.
Ions moving down a gradient release energy but when they move up a gradient it takes energy. Thylakoids are arranged in stacks of disks called granules present on the surface of the stroma. 10 Can you use ETC after example.
The combined action of the entire photosynthetic electron transport chain also produces a proton-motive force that is used to generate ATP. 8 Why is ATP so important. Proton motive force powers ATP synthase in thylakoid membrane What happens in PS I.
What does proton pump do. It is the site of a light-dependent process of photosynthesis. Proton pump is a membrane-integrated enzymatic complex which is able to mobilize protons to generate a proton gradient across the membrane.
Each time water is oxidized two H ions protons remain in the thylakoid space The electrons move from carrier to carrier via redox reactions along the ETC. The ions release energy by moving down gradient but since their moves move upwards gradient energy becomes needed. Net translocation of protons across the membrane is achieved both chemically in photosystem II and by pumping in cytochrome b6f.
Why do Thylakoids arrange in stacks. 3 What is ETC and what does it do. 4 How is ATP made and used in photosynthesis.
Proton Pump and Photosynthesis IMPORTANT Proton Pumps. Ions moving down a gradient release energy but when they move up a gradient it takes energy. For each pair of electrons transported two protons are transferred across the thylakoid membrane at photosystem II and two to four protons at the cytochrome bf complex.
This proton pump is driven by electron transport and catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. The high concentration of hydrogen ions pumped into the inner thylakoid space the thylakoid lumen can then be used to make ATP by a process called chemiosmosis. Does Photosynthesis Use Proton Pump.
What Does The Proton Pump Do. ATP synthase brings out the formation of ATP at the time of light-reaction photosynthesis. The proton gradient on breaking down causes a conformational change in the F1 portion which leads the ATPase enzyme to produce many molecules of ATP.
1 the transport of two electrons and two protons by the diffusion of plastoquinone FROM the stroma side. Photosystem I PSI or plastocyaninferredoxin oxidoreductase is one of two photosystems in the photosynthetic light reactions of algae plants and cyanobacteria. Up to 10 cash back Proton pump is a membrane-integrated enzymatic complex which is able to mobilize protons to generate a proton gradient across the membrane.
3 What is ATP energy in photosynthesis. 9 How do you use ETC correctly. Proton pumps are a special kind of transporter that push hydrogen ions from areas of low concentration to areas with high concentration.
9 What is the role of ATP and Nadph in photosynthesis. A series of rotational shifts and actions take place to make this conformational change occur. P700 accepts an electron passed down from PS II via the electron transport chain.
The process of ATP synthesis during the cellular respiration simultaneously pairs with an electrochemical. Electron transport drives this proton pump which catalyzes the transfer of electrons from plastoquinol to plastocyanin. Powers a proton pump within the chain that generates a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
What drives the proton pump within the thylakoid membrane during photosynthesis. As one of the primary reasons for cell respiration and photosynthesis is the role played by the proton pump. This proton gradient constitutes a fundamental energy reservoir.
6 What is the role of ATP in the chloroplast. Since four protons are needed to drive the synthesis of one molecule of ATP passage of each pair of electrons through photosystems I and II by noncyclic electron flow yields between 1 and 15. 6 What does ETC mean in photosynthesis.
At A Proton Pump Of The Thylakoid Membrane
Is Atp Synthase A Proton Pump Quora

Photosynthesis Of Atp Electrons Proton Pumps Rotors And Poise Cell
Comments
Post a Comment